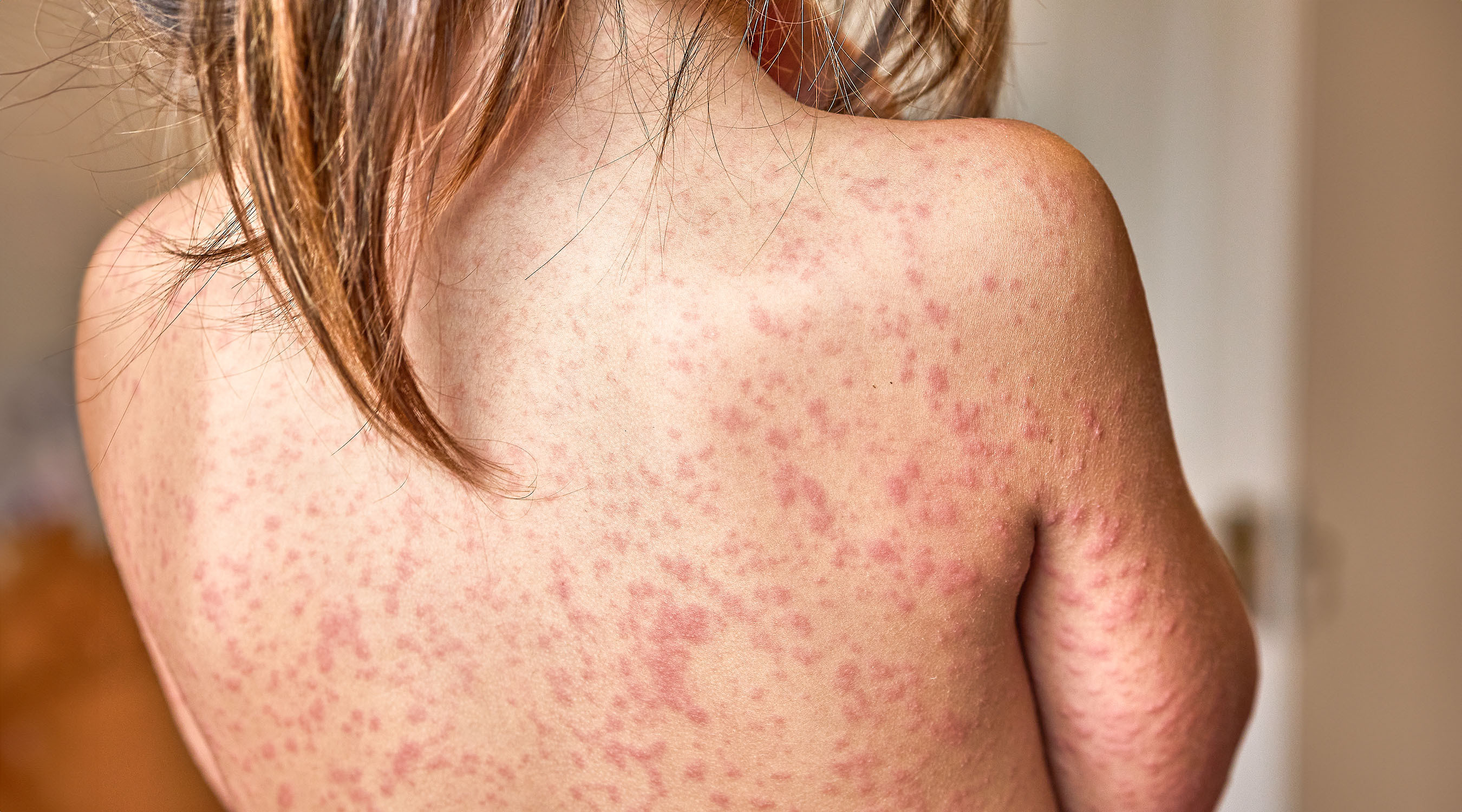
Acute urticaria is often triggered by an infection, but can also occur as a symptom of an allergy. This usually lasts a few hours to days and usually does not require clarification. The trigger of chronic urticaria is often difficult to determine; allergies are rarely the cause. Mechanical (pressure, scratching) or physical stimuli (heat, cold) often play a role. Urticaria can also be exacerbated by physical or psychological stress. In the case of chronic urticaria, a specialist examination is advisable. However, often no cause is found.
Treatment of urticaria
Antihistamines are the basis of therapy. These must sometimes be taken in high doses for weeks to months. For severe forms of urticaria that do not respond adequately to antihistamines, treatment with the IgE antibody omalizumab (Xolair) is an option.
The form of therapy and dosage must be determined individually with each patient and adjusted if necessary. The dermatology team at Dermanence is there for you. Together we will select the optimal form of therapy for you.